Chapter 1 — Beginning the AI Journey | Basics of AI, ML & DL
🚶🏻➡️ Beginning of AI Learning
Year 2023 was the year of Artificial Intelligence. It wasn’t that AI had just been invented — it had lived quietly in research labs and software systems for decades.
But when Generative AI arrived, everything changed. Machines began to write, draw, compose, and even converse. For the first time, intelligence felt alive in the digital world.
Tensor Owl  had always been fascinated by the idea of Artificial Intelligence. Tensor Owl had also been confused between the terms AI, Machine Learning, and Data Science. He often used them interchangeably, so as he began his AI learning journey, the first thing he wanted to understand was the difference between these three.
had always been fascinated by the idea of Artificial Intelligence. Tensor Owl had also been confused between the terms AI, Machine Learning, and Data Science. He often used them interchangeably, so as he began his AI learning journey, the first thing he wanted to understand was the difference between these three.
🤷🏻 Clearing the Confusion
One evening, Tensor Owl was watching his child build a small LEGO car. The child tried different combinations — changing the wheels, adjusting the base, fixing parts that fell off, and improving the design with every attempt.
Tensor Owl saw his child learning from every attempt—each mistake, each correction, each improvement—slowly becoming better. As he watched, a simple realisation formed. His child wasn’t following any fixed rules; he was learning entirely from past experience.
Every successful attempt taught him what worked. This reminded Tensor Owl of the core idea behind Artificial Intelligence—a system showing sensible behaviour that improves over time. The way his child was learning, through trial and error and experience, matched Machine Learning, where systems improve not through rules but through repeated examples.
And when the task got more complex, with many small pieces working together, he related that to Deep Learning, which learns many connected patterns at once.
Watching this small moment at home helped Tensor Owl understand the concepts he had mixed up for years. But he also knew that real AI systems work in a more structured, technical way.
🧠 Understanding the Concepts
The simple LEGO moment helped Tensor Owl connect the ideas in a natural way. But to build a strong foundation, he needed a clearer understanding of what these terms meant in the technical world.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence is a technique that turn machines to work and act in ways that resemble human intelligence.
There are three types of Artificial Intelligence:
 Weak AI (Narrow AI):
Weak AI (Narrow AI):
Weak AI refers to systems designed to perform one specific task very well — but only that task. These systems cannot think like humans, cannot understand the world, and cannot switch tasks on their own.
Examples: Siri or Alexa, spam filters in email, shopping or movie recommendations, face unlock, Google Maps directions.
 General AI:
General AI:
General AI refers to machines with intelligence equivalent to human intelligence. These systems would be able to understand, learn, and perform any task a human can — not just one specific task. They would be capable of reasoning, adapting, making decisions in new situations, and applying knowledge across different domains, similar to how humans think and learn.
Status: General AI is hypothetical. No existing system matches the full range of human cognitive abilities.
A well-known example of General AI can be seen in Sonny from I, Robot, who shows human-level reasoning, learning, and decision-making.
 Superintelligent AI (ASI):
Superintelligent AI (ASI):
Superintelligent AI refers to a hypothetical form of AI that would surpass human intelligence in every aspect — creativity, problem-solving, reasoning, decision-making, and general wisdom. Such a system would outperform humans in all domains, not just specialized tasks.
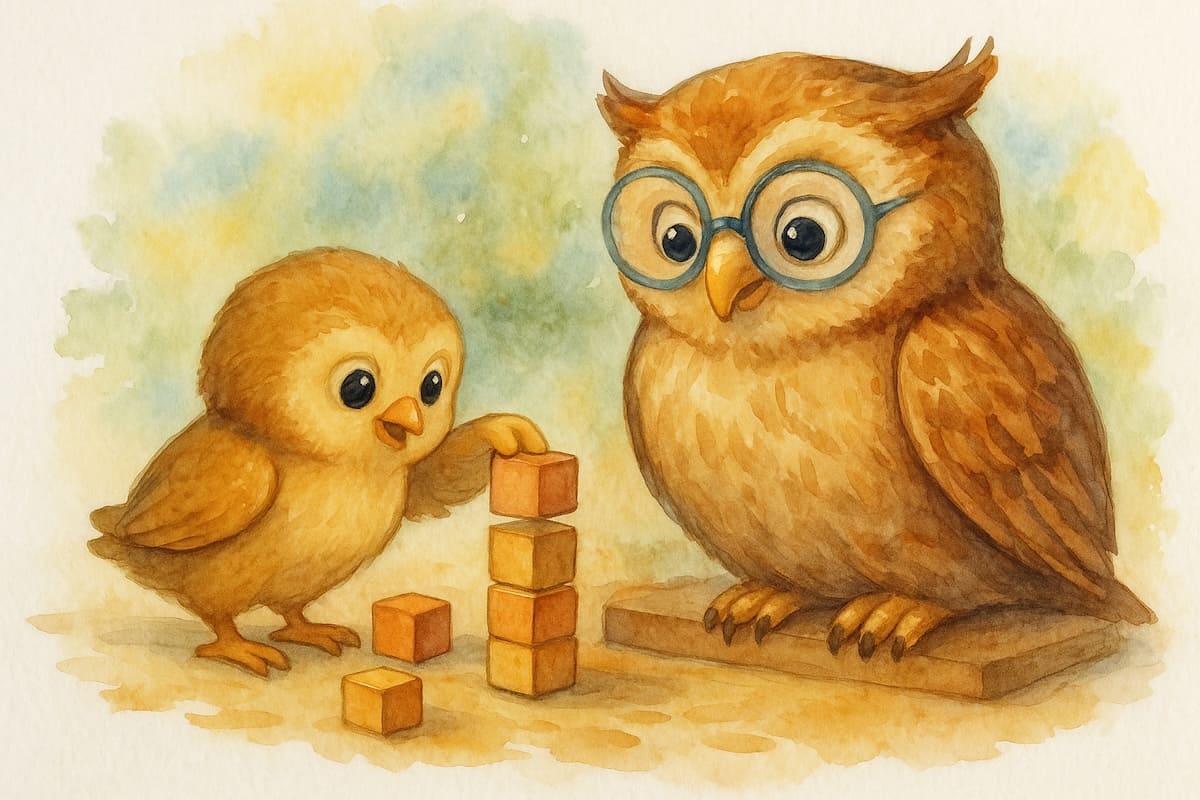
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a branch of AI that focuses on allowing machines to learn from data and experience — just like humans learn from past attempts. It helps systems identify patterns and gradually improve their accuracy. ML also provides statistical tools to explore, analyse, and understand data.
Just like Tensor Owl’s child learned the LEGO patterns by trying, failing, and improving, Machine Learning models improve through repeated examples and feedback.
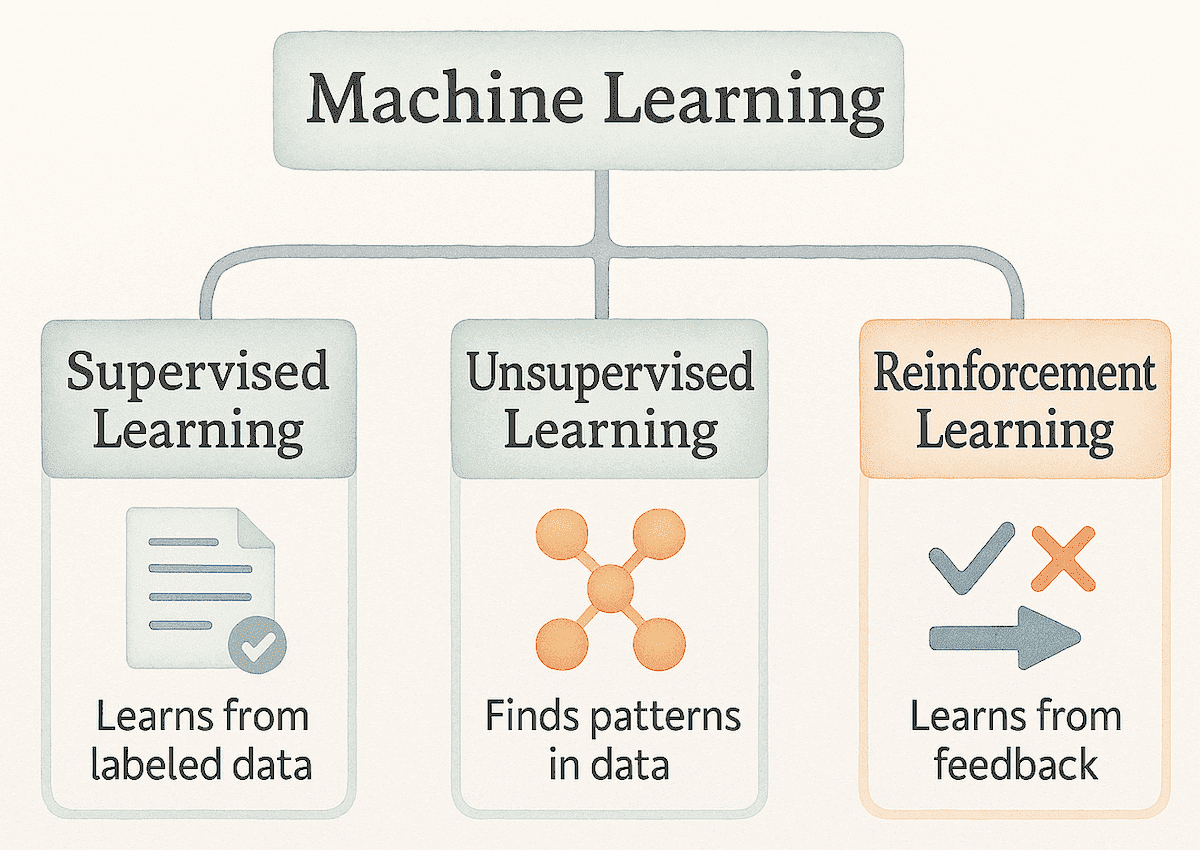
There are three types of Machine Learning:
 Supervised Learning:
Supervised Learning:
Machines are trained using labelled data — data that already contains the correct answers. The system learns by checking its guesses against these correct answers and gradually adjusting itself. The goal here is to develop a system that can accurately predict the outcomes for new, unseen data.
Example: If we give the system sample data that includes height, weight, and the obesity status (whether a person is obese or not), it can learn the pattern behind these. Over time, the system understands the relationship between height, weight, and the category, and then it can classify whether a new person falls into the obese category.
 Unsupervised Learning:
Unsupervised Learning:
Machines learn from data that has no labels and no predefined categories. The system is not told what each item means — instead, it studies the data and discovers hidden patterns and structures on its own. The goal here is to find natural groupings or relationships within the data.
Example: Gmail automatically groups your emails into Primary, Social, Promotions, Updates, and Forums. The system clusters similar emails together without any labelled responses or predefined categories.
 Reinformcement Learning:
Reinformcement Learning:
Machines learn by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties. The system tries different actions, observes the results, and gradually improves its behaviour through trial and error. The goal is to improve behaviour over time by learning what works and what doesn’t.
Example: Google Maps adjusts its route suggestions by learning from drivers’ actions. If a suggested route consistently leads to faster travel, that acts like positive feedback. If many drivers slow down or switch to another route, it acts like negative feedback. Over time, Maps learns which routes work best — not because someone told it the answer, but because it learned from feedback.
Deep Learning
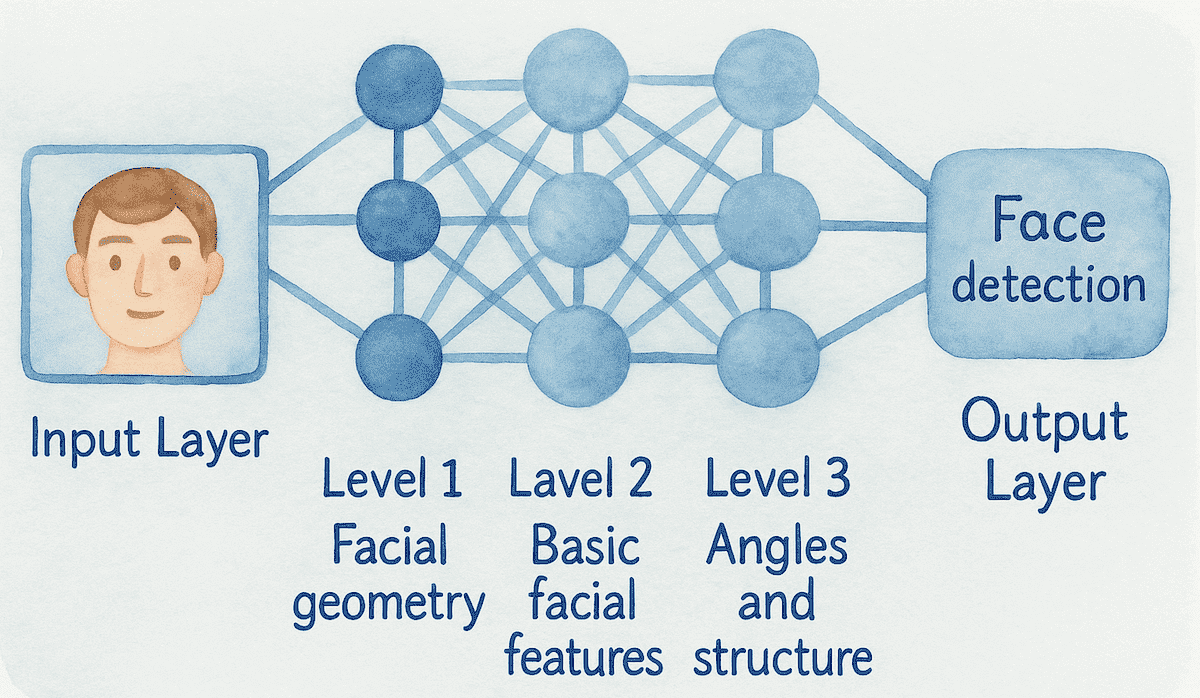
Deep Learning is an advanced part of Machine Learning where systems learn using neural networks made of many layers. Each layer learns something small, and together they build a deeper understanding of the data — just like how humans learn gradually. When we learn something new, we don’t understand everything at once. We notice simple details first, then combine them to make sense of bigger patterns.
In Deep Learning, we build a multi-layer neural network architecture where the early layers learn simple patterns, the middle layers combine them, and the deeper layers understand the final meaning. By moving step-by-step from small details to complete ideas, the network gradually learns complex concepts — just like we do.
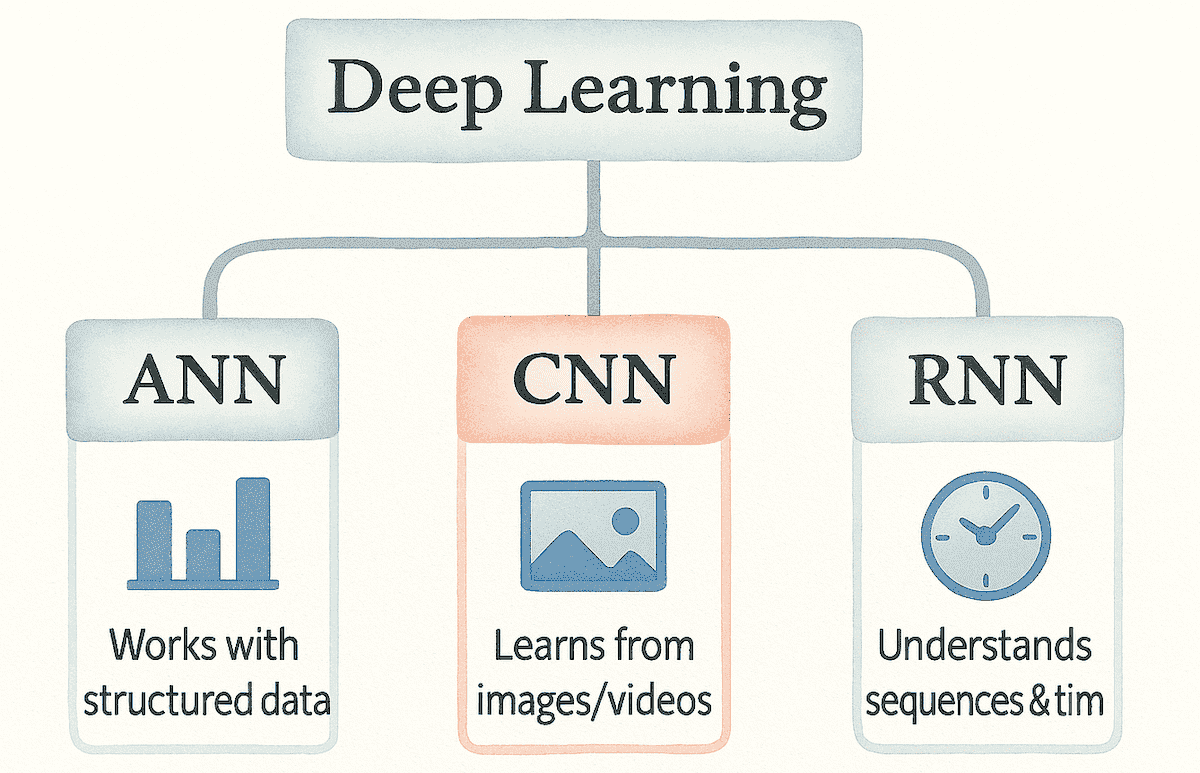
There are three types of Deep Learning:
 Artificial Neural Network (ANN):
Artificial Neural Network (ANN):
ANNs are the foundation of deep learning — simple, layered networks where data flows straight from input to output. They are used for structured data like numbers, tables, and business records. ANNs learn relationships between inputs and outputs to make predictions or classifications. The goal here is to learn the mathematical relationship between the input variables and the target output.
Example: Predicting house prices by learning how factors like area, number of amenities, number of bedrooms, location scores, and past sale values influence the final price.
 Convolutional Neural Network (CNN):
Convolutional Neural Network (CNN):
CNNs are designed for visual understanding — they learn patterns from images and videos. The early layers detect simple features like edges and curves, while deeper layers recognize shapes and complete objects. The goal here is to learn visual features step-by-step, from basic details to full objects.
Example: Identifying whether an image contains a cat or a dog by learning features such as fur texture, ear shape, eye pattern, and overall body structure.
 Recurrent Neural Network (RNN):
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN):
RNNs are designed for sequence-based data — anything that comes in order, such as text, speech, or time-series signals. They remember information from previous steps, allowing them to understand context and patterns that unfold over time. The goal here is to learn how current data depends on what came before.
Example: Predicting the next word in a sentence by remembering the words that came before, such as completing “The sun rises in the…” with “east.”
🧾 Summary
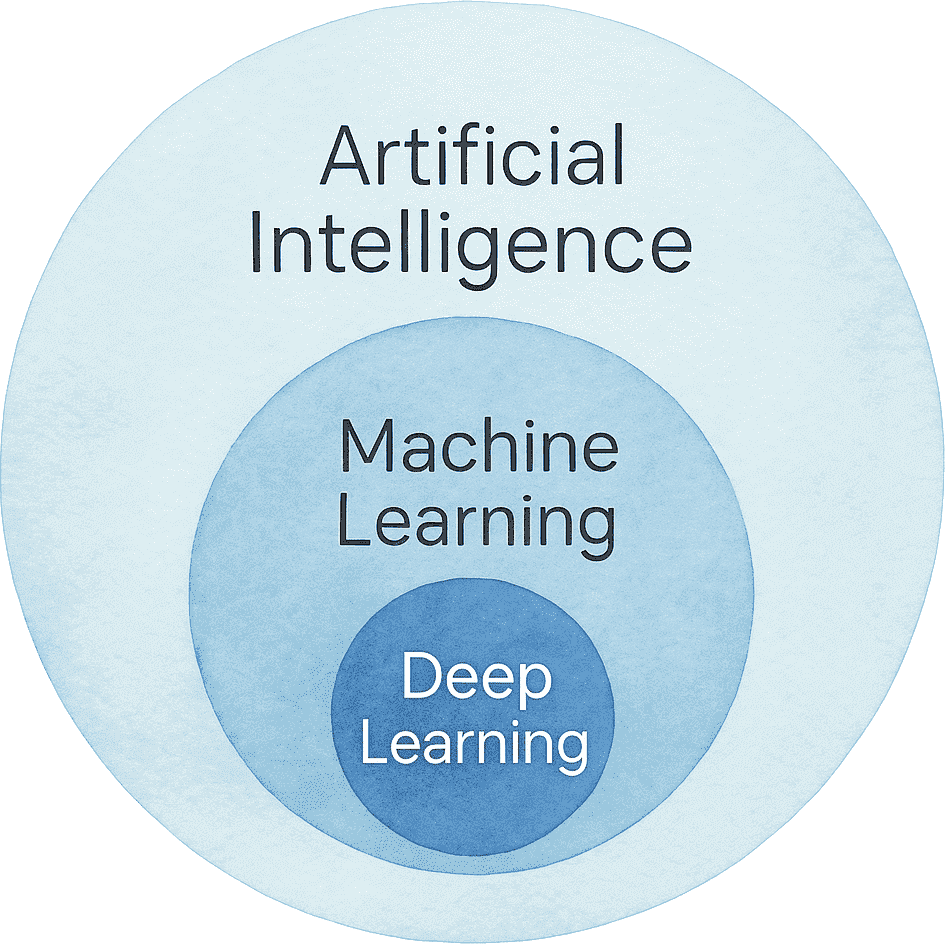
 Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad idea of creating machines that show human-like intelligence.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broad idea of creating machines that show human-like intelligence.
 Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI where systems learn from data and improve through experience.
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI where systems learn from data and improve through experience.
 Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of ML that learns using multi-layer neural networks, discovering patterns step-by-step.
Deep Learning (DL) is a subset of ML that learns using multi-layer neural networks, discovering patterns step-by-step.
 Machine Learning has three learning types: Supervised, Unsupervised, and Reinforcement Learning.
Machine Learning has three learning types: Supervised, Unsupervised, and Reinforcement Learning.
 Deep Learning has three major architectures: ANN, CNN, and RNN, each suited to a different kind of pattern.
Deep Learning has three major architectures: ANN, CNN, and RNN, each suited to a different kind of pattern.
Summary – Voice Recording
🧩 Conclusion
This is the beginning of the Artificial Intelligence journey for Tensor Owl  . By exploring AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning step-by-step, Tensor Owl realised that these ideas are not complex at all. They follow the same natural learning patterns we see in life itself — noticing, practicing, combining, and gradually improving.
. By exploring AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning step-by-step, Tensor Owl realised that these ideas are not complex at all. They follow the same natural learning patterns we see in life itself — noticing, practicing, combining, and gradually improving.
With this basic understanding in place, Tensor Owl is now ready to move deeper — into how neural networks learn, how models are trained, and how machines make decisions.
Chapter 2(Coming soon) begins the real exploration of how Machines Learn — the heart of modern AI.
🔎 Recap & Reflection
Which situation best reflects machine learning?
An AI system is designed only to translate text from one language to another. Which type of AI does this represent?
A model is trained on past house prices using area, so it can predict the price of a new house. What learning method does this situation reflect?
A robot tries different moves in a game and gets rewards when it makes good decisions. Over time, it plays better. What type of learning is happening?
An online store wants to develop a model that can automatically group customers based on their buying behavior without any predefined categories. What kind of learning does this represent?
A school uses a small neural network to predict which students may achieve merit. The first layer uses features like past scores and attendance, while the next layer weights study hours more strongly to enhance the prediction. What type of model is this?
A neural network is trained using thousands of labeled images to recognize cats. What does this scenario represent?


Comments powered by Disqus.